Electron Backscatter Diffraction - EBSD
What is EBSD?
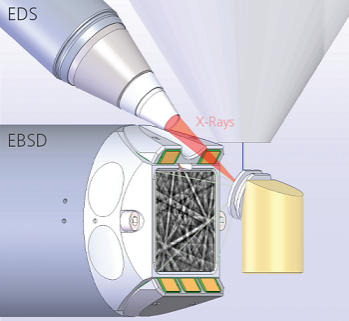
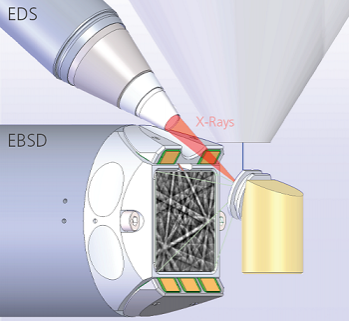
EBSD is a scanning electron microscope (SEM) based technique for materials characterisation. In EBSD, the electron beam is scanned across the surface of a tilted crystalline sample; the diffracted electrons at each point form a pattern that can be detected and then analysed using dedicated hardware and software. At each point the indexing process provides information about the phase and the crystallographic orientation from which the microstructure can be effectively reconstructed. This enables a full characterisation of the microstructural properties of the sample. EBSD is now fast and fully automated, making it a powerful tool in many industries and research fields, as shown in the table below.
More information about the EBSD technique and its applications can be found on the educational website, ebsd.com.
The Oxford Instruments AZtec EBSD system combines the speed and sensitivity of the world's only all-in-one EBSD detector, Symmetry S3, the superior analytical performance of the AZtecHKL acquisition software and the powerful, modern data processing capabilities of AZtecCrystal to create the market’s leading tool for EBSD analysis.